1. std I/O Code:
stdin: 0 #input read from keyboard on default
stdout:1 #info write
stderr:2 #error write
any :n #input or output from anywhere.
============================
1. [n] < $file or stdin #read from $file or stdin to [n].
2. [n] > content.txt #new write to content.txt
3. [n] >> content.txt #append write to content.txt
4. &> content.txt
stdout:1 #info write
stderr:2 #error write
any :n #input or output from anywhere.
============================
1. [n] < $file or stdin #read from $file or stdin to [n].
2. [n] > content.txt #new write to content.txt
3. [n] >> content.txt #append write to content.txt
4. &> content.txt
>& content.txt
#same means of new write content.txt from stdout and stderr.
============================
Examples:
$ ./test.sh >info.log #stdout log to info.log
$ ./test.sh 1>info.log #same as the above. 1> is same as >, 1 can be omited.
$ ./test.sh 2>error.log #stderr error only to error.log, stdout info to screen
$ ./test.sh >& result.log #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh &> result.log #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh > result.log 2>&1 #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh 1> info.log 2>error.log #stdout to info.log, stderr to error.log
============================
Examples:
$ ./test.sh >info.log #stdout log to info.log
$ ./test.sh 1>info.log #same as the above. 1> is same as >, 1 can be omited.
$ ./test.sh 2>error.log #stderr error only to error.log, stdout info to screen
$ ./test.sh >& result.log #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh &> result.log #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh > result.log 2>&1 #stdout and stderr to result.log
$ ./test.sh 1> info.log 2>error.log #stdout to info.log, stderr to error.log
Omit: >/dev/null
$ ./test.sh >& /dev/null
$ ./test.sh &> /dev/null
$ ./test.sh > /dev/null 2>&1
$ ./test.sh 1> /dev/null 2>/dev/null
2>&1: Means copy stdout to stderr. reference 1 in 2.
======================================
2. To Screen And File Meanwhile By Command: tee
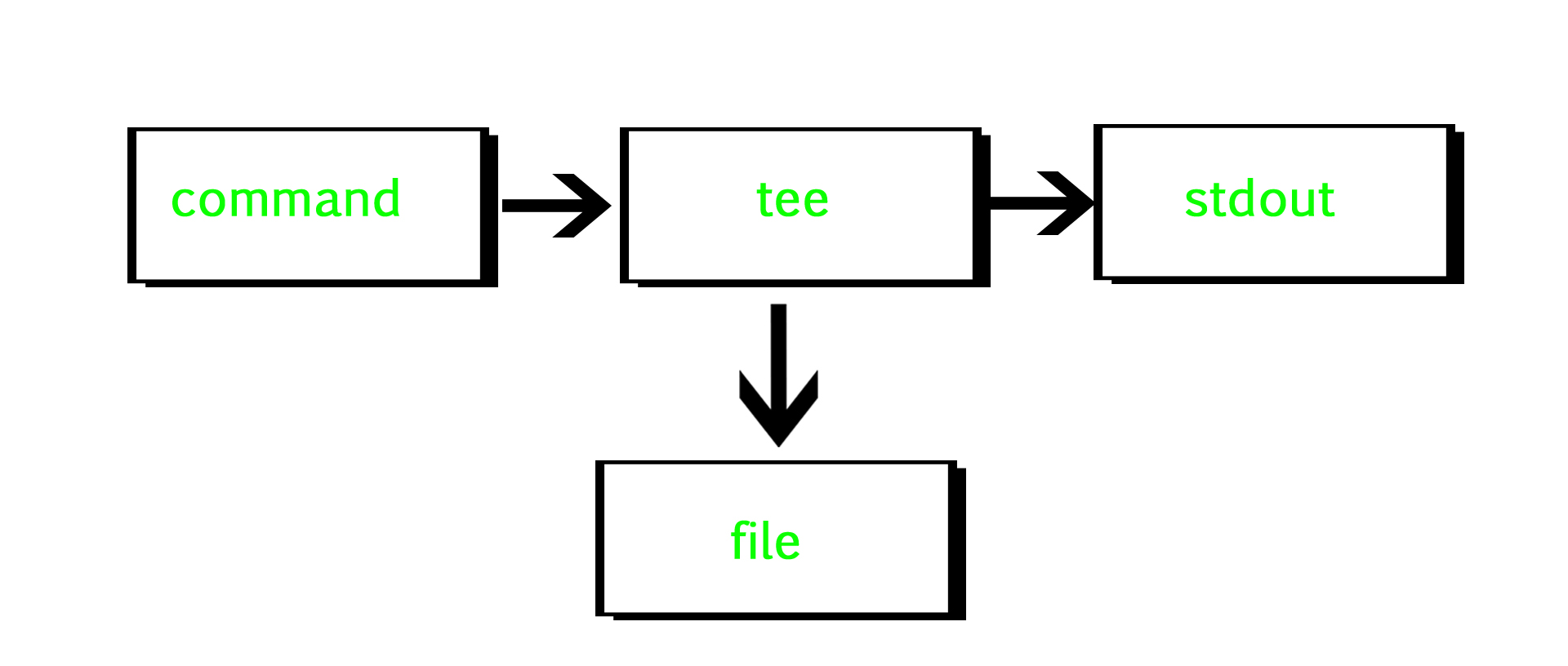
tee command reads the standard input and writes it to both the standard output and one or more files.
$ tee --help
Usage: tee [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Copy standard input to each FILE, and also to standard output.
-a, --append append to the given FILEs, do not overwrite
-i, --ignore-interrupts ignore interrupt signals
-p diagnose errors writing to non pipes
--output-error[=MODE] set behavior on write error. See MODE below
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
MODE determines behavior with write errors on the outputs:
'warn' diagnose errors writing to any output
'warn-nopipe' diagnose errors writing to any output not a pipe
'exit' exit on error writing to any output
'exit-nopipe' exit on error writing to any output not a pipe
The default MODE for the -p option is 'warn-nopipe'.
The default operation when --output-error is not specified, is to
exit immediately on error writing to a pipe, and diagnose errors
writing to non pipe outputs.
# copy stderr to stdout, and out to screen meanwhile result.log.
$ ./test.sh |& tee result.log
$ ./test.sh 2>&1 | tee result.log
#stderr to stderr.log, stdout to stdout.log. meanwhile to screen.
$ { { .test.sh | tee stdout.log 1>&3; } 2>&1 | tee stderr.log 1>&2; } 3>&1
#expression:
1>&3: rediection 1 to 3, temp setting stdout to &3, for display 3 to screen
2>&1 | tee: redirection 2 to 1, and tee to stderr.log
没有评论:
发表评论